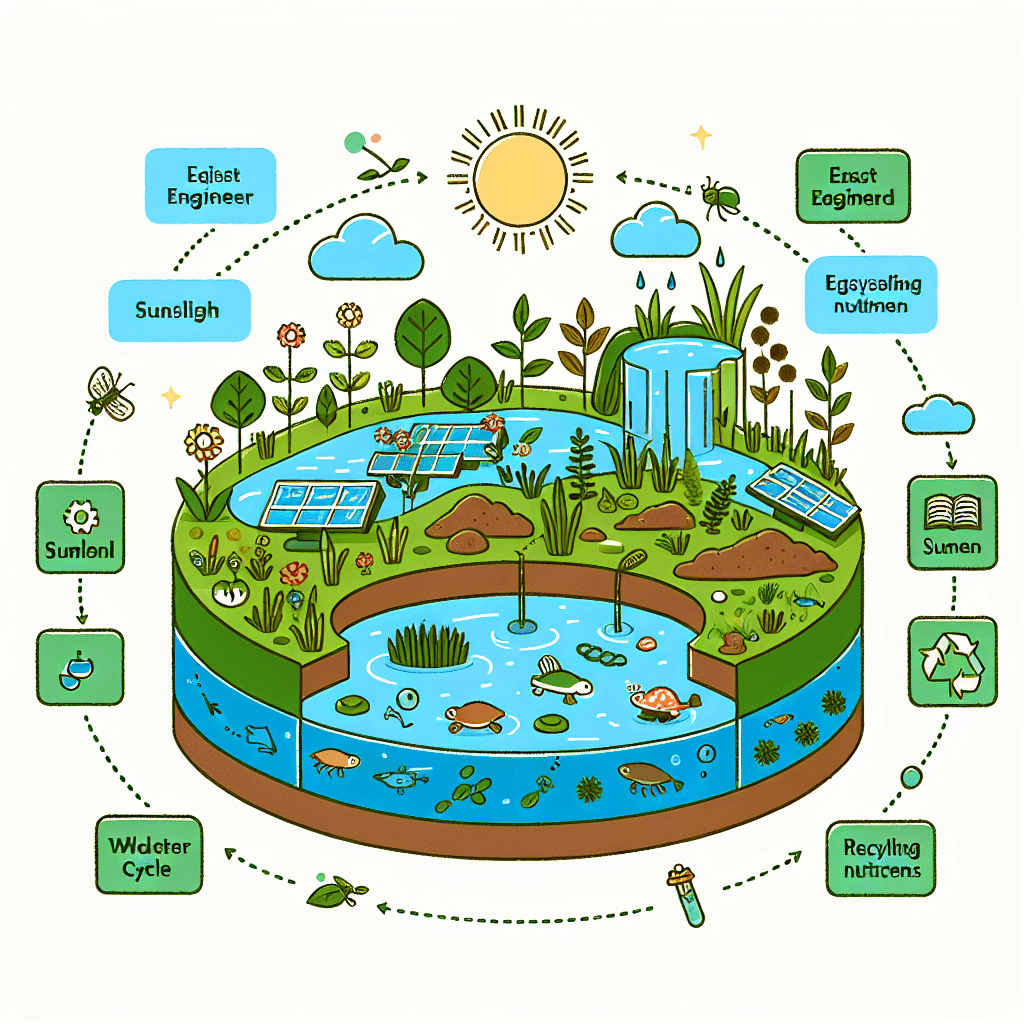
Ecosystem Engineers: Design a Self-Sustaining Ecosystem Model
Inquiry Framework
Question Framework
Driving Question
The overarching question that guides the entire project.How can we design a model ecosystem where organisms interact as ecosystem engineers to demonstrate a sustainable flow of energy and cycling of matter?Essential Questions
Supporting questions that break down major concepts.- How do organisms interact within an ecosystem to create a flow of energy and cycling of matter?
- What factors can disrupt the balance of an ecosystem, and how do ecosystem engineers help maintain stability?
- How can we model the flow of energy and cycling of matter in a self-sustaining ecosystem?
- What are the key components of a balanced ecosystem, and how do they rely on each other?
- How do ecosystem engineers impact the flow of energy and cycling of matter within their environment?
Standards & Learning Goals
Learning Goals
By the end of this project, students will be able to:- Students will be able to design a self-sustaining ecosystem model.
- Students will be able to describe the flow of energy and cycling of matter in an ecosystem.
- Students will be able to explain how organisms interact as ecosystem engineers to maintain ecosystem stability.
NGSS
Entry Events
Events that will be used to introduce the project to students"Mystery Box Ecosystem"
Students receive a sealed box with limited visibility. Inside, they observe initial biotic and abiotic components. The challenge is to infer the system's potential, predict energy flow, and pose questions about sustainability, sparking initial ecosystem investigations.Portfolio Activities
Portfolio Activities
These activities progressively build towards your learning goals, with each submission contributing to the student's final portfolio.Energy Flow Diagram Designer
Students will design a visual diagram that models the flow of energy through different trophic levels in the ecosystem.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA labeled diagram illustrating the flow of energy through the ecosystem, complete with annotations explaining the processes involved.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity directly supports MS-LS2-3 by requiring students to visually represent and explain the flow of energy among living parts of an ecosystem.Matter Cycling Storyboard Artist
Students will create a storyboard that illustrates how matter cycles through the ecosystem, focusing on key elements like carbon, water, and nitrogen.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA storyboard illustrating the cycling of matter through the ecosystem, with clear visuals and captions explaining each stage of the process.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity supports MS-LS2-3 by focusing on the cycling of matter within the ecosystem, requiring students to describe how key elements move among the living and nonliving components.Self-Sustaining Ecosystem Model Design Proposal
Students will create a design proposal for their self-sustaining ecosystem model, detailing its components, interactions, and sustainability mechanisms.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA detailed design proposal, including a written description and diagram, outlining the components, interactions, and sustainability mechanisms of their model ecosystem.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity synthesizes MS-LS2-3 by requiring students to apply their knowledge of energy flow and matter cycling to design a functional ecosystem model.Ecosystem Stability Challenge: Scenario Analysis
Students will analyze various scenarios that could disrupt their model ecosystem, predicting the consequences and proposing solutions to maintain stability.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA scenario analysis report detailing potential disruptions to the model ecosystem, their consequences, and proposed solutions for maintaining stability.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity reinforces MS-LS2-3 by challenging students to think critically about the factors that affect ecosystem stability and apply their understanding of energy flow and matter cycling to problem-solving.Ecosystem Component Cataloger
Students will create a detailed catalog of biotic and abiotic components, including their roles and interactions related to energy flow and matter cycling.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA detailed catalog presented in a well-organized table, showcasing various ecosystem components and their functional roles.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity aligns with MS-LS2-3 by requiring students to identify and describe the various living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem, which is fundamental to understanding matter cycling and energy flow.Ecosystem Engineer Impact Report
Students will research and report on how specific organisms act as ecosystem engineers, influencing energy flow and matter cycling.Steps
Here is some basic scaffolding to help students complete the activity.Final Product
What students will submit as the final product of the activityA comprehensive report detailing how the chosen organism acts as an ecosystem engineer and how its actions affect energy flow and matter cycling.Alignment
How this activity aligns with the learning objectives & standardsThis activity extends MS-LS2-3 by focusing on the role of specific organisms in influencing energy flow and matter cycling, promoting a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics.Rubric & Reflection
Portfolio Rubric
Grading criteria for assessing the overall project portfolioEcosystem Model Design and Analysis Rubric
Energy Flow Representation
Assesses the student's ability to accurately represent and explain the flow of energy through different trophic levels in the ecosystem model.Trophic Level Identification
Accuracy in identifying and labeling the different trophic levels (producers, consumers, decomposers) within the ecosystem.
Exemplary
4 PointsAccurately identifies and comprehensively labels all trophic levels, including specific examples of organisms within each level.
Proficient
3 PointsAccurately identifies and labels most trophic levels with relevant examples.
Developing
2 PointsIdentifies some trophic levels but may have inaccuracies or omissions in labeling.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to identify and label trophic levels; demonstrates significant misunderstandings.
Energy Transfer Diagram
Clarity and accuracy of the diagram (food web, energy pyramid) in illustrating energy transfer between trophic levels.
Exemplary
4 PointsDiagram clearly and accurately illustrates energy transfer with appropriate arrows and labels, demonstrating a deep understanding of energy flow.
Proficient
3 PointsDiagram accurately illustrates energy transfer with clear labels and arrows.
Developing
2 PointsDiagram illustrates energy transfer but may have some inaccuracies or unclear representations.
Beginning
1 PointsDiagram is incomplete, inaccurate, or fails to illustrate energy transfer effectively.
Explanation of Energy Transfer
Quality and depth of annotations explaining how energy is transferred and transformed at each trophic level.
Exemplary
4 PointsAnnotations provide comprehensive and insightful explanations of energy transfer and transformation processes (photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition) at each level.
Proficient
3 PointsAnnotations clearly explain energy transfer and transformation processes at each level.
Developing
2 PointsAnnotations provide basic explanations of energy transfer but may lack depth or accuracy.
Beginning
1 PointsAnnotations are minimal, unclear, or fail to explain energy transfer processes effectively.
Matter Cycling Illustration
Assesses the student's ability to illustrate and explain the cycling of matter (carbon, water, nitrogen) within the ecosystem model.Key Element Selection
Appropriateness and relevance of the chosen key element(s) (carbon, water, nitrogen) to the ecosystem model.
Exemplary
4 PointsSelects a key element and justifies its importance in the ecosystem with insightful reasoning.
Proficient
3 PointsSelects a relevant key element and explains its importance in the ecosystem.
Developing
2 PointsSelects a key element, but the explanation of its importance may be unclear or incomplete.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to select a relevant key element or explain its role in the ecosystem.
Stage Identification
Accuracy in identifying and dividing the cycling pathway into key stages (photosynthesis, decomposition, respiration, etc.).
Exemplary
4 PointsAccurately identifies and comprehensively explains all key stages of the cycling pathway, demonstrating a deep understanding of matter cycling.
Proficient
3 PointsAccurately identifies and explains most key stages of the cycling pathway.
Developing
2 PointsIdentifies some stages of the cycling pathway but may have inaccuracies or omissions.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to identify key stages of the cycling pathway; demonstrates significant misunderstandings.
Storyboard Clarity and Accuracy
Clarity and accuracy of the storyboard panels in illustrating the cycling process at each stage.
Exemplary
4 PointsStoryboard panels are visually clear, accurate, and effectively illustrate the cycling process at each stage with detailed captions.
Proficient
3 PointsStoryboard panels are clear and accurately illustrate the cycling process at each stage with descriptive captions.
Developing
2 PointsStoryboard panels illustrate the cycling process but may lack clarity or accuracy in some areas.
Beginning
1 PointsStoryboard panels are incomplete, inaccurate, or fail to illustrate the cycling process effectively.
Ecosystem Model Design and Sustainability
Assesses the student's ability to design a self-sustaining ecosystem model with appropriate components, interactions, and sustainability mechanisms.Component Selection
Appropriateness and justification of the biotic and abiotic components selected for the model ecosystem.
Exemplary
4 PointsSelects components that are highly appropriate for a self-sustaining ecosystem and provides detailed justifications for their inclusion based on their roles in energy flow and matter cycling.
Proficient
3 PointsSelects appropriate components for a self-sustaining ecosystem and provides clear justifications for their inclusion.
Developing
2 PointsSelects some appropriate components but may have omissions or unclear justifications.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to select appropriate components or justify their inclusion in the model ecosystem.
Interaction Description
Clarity and depth of the description of interactions between components, emphasizing energy flow and matter cycling.
Exemplary
4 PointsProvides a comprehensive and insightful description of interactions, clearly explaining how they contribute to energy flow and matter cycling within the model ecosystem.
Proficient
3 PointsProvides a clear description of interactions and explains their contribution to energy flow and matter cycling.
Developing
2 PointsDescribes some interactions but may lack clarity or depth in explaining their contribution to energy flow and matter cycling.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to describe interactions or explain their role in energy flow and matter cycling.
Sustainability Mechanisms
Effectiveness and feasibility of the mechanisms proposed to ensure the model ecosystem is self-sustaining.
Exemplary
4 PointsProposes highly effective and feasible sustainability mechanisms that address key challenges and ensure long-term stability of the model ecosystem.
Proficient
3 PointsProposes effective sustainability mechanisms that contribute to the stability of the model ecosystem.
Developing
2 PointsProposes some sustainability mechanisms, but their effectiveness or feasibility may be questionable.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to propose effective sustainability mechanisms for the model ecosystem.
Diagram/Sketch Quality
Quality and clarity of the diagram or sketch of the proposed model ecosystem, including labeling of components and interactions.
Exemplary
4 PointsDiagram/sketch is visually clear, detailed, and accurately represents all components and interactions within the model ecosystem with comprehensive labeling.
Proficient
3 PointsDiagram/sketch is clear and accurately represents components and interactions with appropriate labeling.
Developing
2 PointsDiagram/sketch represents some components and interactions but may lack clarity or detail.
Beginning
1 PointsDiagram/sketch is incomplete, inaccurate, or fails to represent components and interactions effectively.
Ecosystem Stability Analysis and Problem-Solving
Assesses the student's ability to analyze potential disruptions to the ecosystem and propose solutions to maintain stability.Disruption Identification
Identification of potential disruptions to the model ecosystem (invasive species, pollution, climate change).
Exemplary
4 PointsIdentifies a wide range of relevant and realistic disruptions with clear explanations of their potential impacts.
Proficient
3 PointsIdentifies several relevant disruptions to the model ecosystem.
Developing
2 PointsIdentifies some disruptions but may lack relevance or detail.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to identify potential disruptions to the model ecosystem.
Consequence Prediction
Accuracy in predicting the consequences of disruptions for energy flow, matter cycling, and overall ecosystem stability.
Exemplary
4 PointsAccurately and comprehensively predicts the consequences of disruptions, demonstrating a deep understanding of ecosystem dynamics and interconnectedness.
Proficient
3 PointsAccurately predicts the consequences of disruptions for energy flow, matter cycling, and ecosystem stability.
Developing
2 PointsPredicts some consequences but may have inaccuracies or omissions.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to predict the consequences of disruptions accurately.
Solution Proposal
Effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed solutions or modifications to mitigate the negative impacts of disruptions.
Exemplary
4 PointsProposes highly effective and feasible solutions that address the root causes of the disruptions and promote long-term ecosystem stability.
Proficient
3 PointsProposes effective solutions that mitigate the negative impacts of disruptions.
Developing
2 PointsProposes some solutions, but their effectiveness or feasibility may be questionable.
Beginning
1 PointsStruggles to propose effective solutions to mitigate the impacts of disruptions.
Report Quality
Organization and clarity of the scenario analysis report, including clear summaries of disruptions, consequences, and proposed solutions.
Exemplary
4 PointsReport is exceptionally well-organized, clearly written, and provides a comprehensive analysis of disruptions, consequences, and proposed solutions with supporting evidence.
Proficient
3 PointsReport is well-organized, clearly written, and provides a thorough analysis of disruptions, consequences, and proposed solutions.
Developing
2 PointsReport is organized but may lack clarity or detail in some areas.
Beginning
1 PointsReport is poorly organized, unclear, or incomplete.
Ecosystem Component Identification and Role Explanation
Assesses student's ability to identify biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem and explain their roles in energy flow and matter cycling.Component Listing
Completeness and accuracy of the list of biotic and abiotic components included in the catalog.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe list includes a comprehensive and diverse range of biotic and abiotic components, demonstrating a thorough understanding of ecosystem composition.
Proficient
3 PointsThe list includes a wide range of common biotic and abiotic components.
Developing
2 PointsThe list includes some biotic and abiotic components, but may be lacking in diversity or completeness.
Beginning
1 PointsThe list is incomplete and lacks a clear understanding of biotic and abiotic components.
Role Description
Clarity and accuracy of the description of each component's role in the ecosystem.
Exemplary
4 PointsDescriptions of each component's role are exceptionally clear, detailed, and accurate, demonstrating a deep understanding of their functions within the ecosystem.
Proficient
3 PointsDescriptions of each component's role are clear and accurate.
Developing
2 PointsDescriptions of some components' roles are provided, but they may lack clarity or detail.
Beginning
1 PointsDescriptions of component roles are unclear, inaccurate, or missing.
Contribution Explanation
Explanation of how each component contributes to either the flow of energy or the cycling of matter within the ecosystem.
Exemplary
4 PointsExplanations of how each component contributes to energy flow or matter cycling are insightful, detailed, and demonstrate a strong understanding of ecosystem processes.
Proficient
3 PointsExplanations clearly describe how each component contributes to energy flow or matter cycling.
Developing
2 PointsExplanations of component contributions are provided, but they may lack clarity or depth.
Beginning
1 PointsExplanations of component contributions are unclear, inaccurate, or missing.
Table Organization
Organization and clarity of the catalog presented in a table format.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe table is exceptionally well-organized, easy to read, and clearly presents all components and their related information.
Proficient
3 PointsThe table is well-organized and clearly presents all components and their related information.
Developing
2 PointsThe table is organized, but may lack clarity or completeness in some areas.
Beginning
1 PointsThe table is poorly organized, difficult to read, or incomplete.
Ecosystem Engineer Analysis and Impact
Assesses student's understanding of how ecosystem engineers influence energy flow and matter cycling.Organism Selection
Appropriateness of the chosen ecosystem engineer for studying its impact on energy flow and matter cycling.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe chosen ecosystem engineer is highly appropriate for studying its impact and the rationale is clearly articulated and insightful.
Proficient
3 PointsThe chosen ecosystem engineer is appropriate and the rationale is clearly articulated.
Developing
2 PointsThe chosen ecosystem engineer is adequate, but the rationale for its selection is weak.
Beginning
1 PointsThe chosen ecosystem engineer is inappropriate or the rationale is missing.
Environmental Modification Description
Accuracy and detail in describing how the chosen organism modifies its environment.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe description of the organism's environmental modifications is exceptionally detailed and accurate, demonstrating a thorough understanding of its activities.
Proficient
3 PointsThe description of the organism's environmental modifications is detailed and accurate.
Developing
2 PointsThe description of the organism's environmental modifications is adequate, but may lack detail.
Beginning
1 PointsThe description of the organism's environmental modifications is incomplete or inaccurate.
Impact Explanation
Explanation of how the organism's activities affect the flow of energy and/or the cycling of matter within the ecosystem.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe explanation of the organism's impact on energy flow and/or matter cycling is insightful, detailed, and demonstrates a strong understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
Proficient
3 PointsThe explanation clearly describes how the organism impacts energy flow and/or matter cycling.
Developing
2 PointsThe explanation of the organism's impact is adequate, but may lack clarity or depth.
Beginning
1 PointsThe explanation of the organism's impact is unclear, inaccurate, or missing.
Report Quality
Overall quality and organization of the report, including specific examples of the organism's impact on its environment and other organisms.
Exemplary
4 PointsThe report is exceptionally well-written, organized, and provides comprehensive evidence of the organism's impact on its environment and other organisms with specific examples.
Proficient
3 PointsThe report is well-written, organized, and provides clear evidence of the organism's impact.
Developing
2 PointsThe report is adequately written and organized, but may lack detail or clarity in some areas.
Beginning
1 PointsThe report is poorly written, disorganized, or incomplete.